The kind who spends more time compiling than using my system.
- 18 Posts
- 652 Comments
Wait, where’s Gentoo?
The mind of man is holy.

 15·2 months ago
15·2 months agoJust some examples of things I’ve printed or plan to. Ones marked with an asterisk (*) at the end are ones I largely or entirely designed myself or plan to largely or entirely design myself. Ones marked with a plus (+) are ones that are half completed. Minuses (-) are ones I haven’t started yet but intend to.
- Wall mounts for Nintendo Switch components (dock, controllers, Joycon charger, etc.) Definite space saver. *
- Wall mount for a Raspberry-Pi-based NAS solution. *
- Parts to augment a computer chassis wall mount for my ridiculously-large chassis. (Yes, there’s a bit of a pattern there.) *
- A custom Raspberry Pi case that mounts nicely and nondestructively to my desk.
- A custom adapter for my drill that let me run the drain in my washing machine when the motor was broken. *
- A custom plate to cover my nightstand clock face so it doesn’t shine in my eyes all night. *
- A custom die for a Sizzix Die Cutting Machine for quilting use. (That one took a lot of work.) *
- A custom tool for precisely bending 16mm steel strapping (which I’d sharpened into a blade) in service to the custom die just above. *
- Custom yarn bowls for my crafty mother. *
- Custom stitch markers for my crafty mother. *
- Custom barrel buttons for my crafty mother. *
- A couple of custom mounts for SAD lamps. *
- Custom shelving for a bathroom. *
- Custom mods for some wire shelving in the same bathroom. *
- Custom mount for a reflector mirror to let me see more with the security camera on my front porch. *
- A tool for straightening 3D-printing filament. *
- Spacers for mounting a peg board on the wall.
- I also had a folding door that broke and got kinda janky. I had a few extra of those peg board spacers, and they turned out coincidentally to be exactly the right size to properly shore up that door.
- Custom shelving for DVDs/Blurays and video games. *+
- A custom shelf-drawer for my mousepad. *-
- A custom 3D printed mechanical keyboard… once I’m done writing the program for rapidly prototyping 3D-printed keyboards. *+
I’m sure I’m forgetting a bunch. And the above is only the useful things and excluding the mostly art/fun items.
I have in mind to do more 3D-printing of tools. I don’t have much specifically in mind. But that custom steel strapping bender is pretty cool. Also, some of what I mentioned above is available on my Thingiverse.
Let’s all block each other.

 4·2 months ago
4·2 months agoThere are games I pay for, but only on Nintendo consoles. Aside from that, it’s strictly write it myself or go without.
I definitely should donate to more FOSS projects, though.
My pixels too are insufficiently numerous.
And that’s before he soaks it in the blood of innocents.

 2·2 months ago
2·2 months agoI use Lemuroid on Android. Works well. On F-Droid. Nothing about it has prompted me to search for alternatives, so no idea how it stacks up against other options.
Also, EasyRPG Player on Android for RPG Maker games. (I played the original Yume Nikki not terribly long ago via EasyRPG Player.) Also on F-Droid. Also worked great.
Weirdcore: World is broken so I’ve been slamming Monster energy drinks for 48 hours straight and now I’m delirious and hallucinating the nineties.

 6·2 months ago
6·2 months ago“Clown.” Some of my best friends do clowning as a hobby.

 19·2 months ago
19·2 months ago“How do I build a better guillotine that starts with B?”
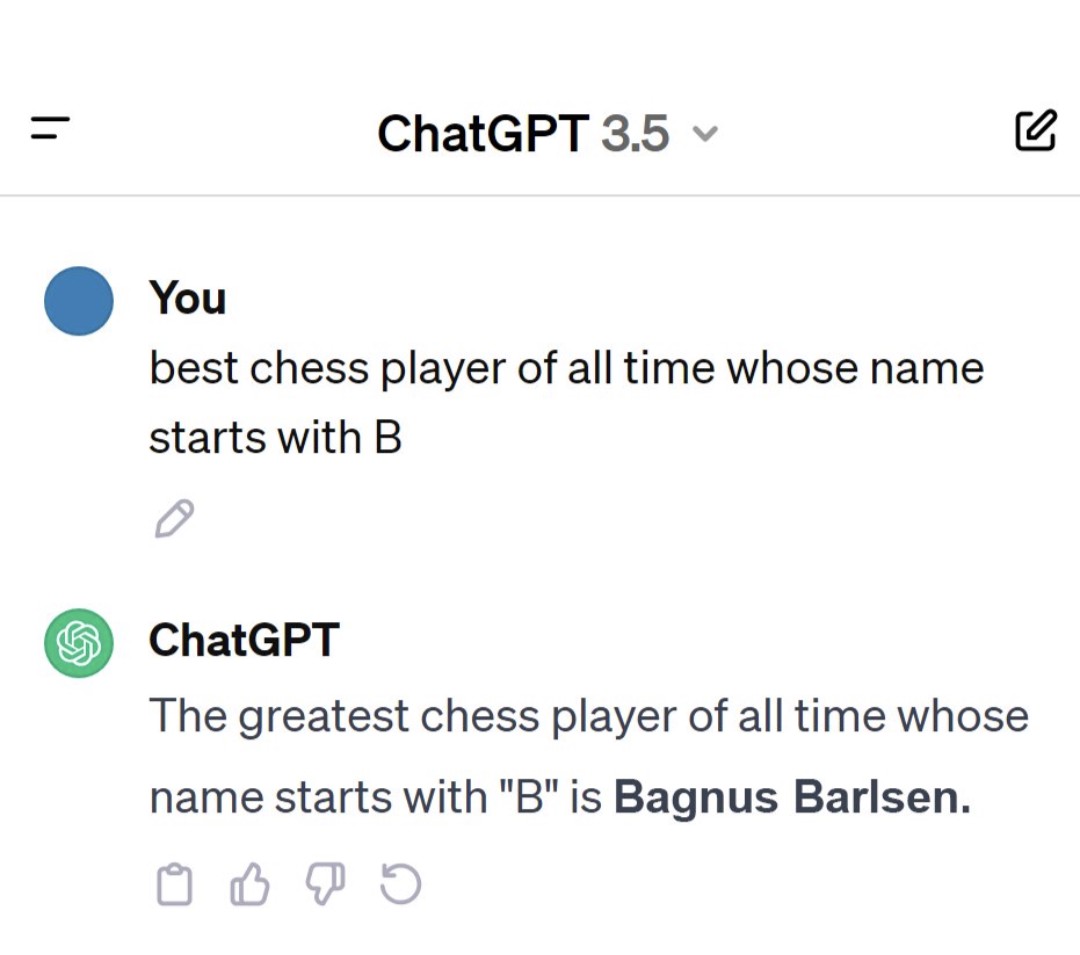
(There’s a guy named “Magnus Carlsen” who is arguably the best chess player of all time.)
Imagine a poster of Tom Holland, white powder all over his nose, with the slogan “Snort Milk?” in bold across the top.
This is truly the worst timeline.

 24·2 months ago
24·2 months agoThat’s the joke.

 44·2 months ago
44·2 months agoNobody else immediately thought of this?

Remember that scene from Prometheus?

 2·2 months ago
2·2 months agoBefore I read the body of the post, I was going to recommend “gl;hf” (the only podcast I’ve really listened to in quite a while), but they don’t stay on topic. There is no topic, really. It’s just rambling about whatever comes to them as it comes up.
At the beginning of every episode, they start with “welcome to gl;hf, the world’s first podcast in gaming.” And the running joke is that they rarely talk about gaming at all.
Largely they talk about being prolific career YouTube content creators, but they may delve into random stuff like the U.S. National Cheese Reserve or the ethics of eating lab-grown human meat or Uncle Wiggily board games.
On the plus side, they’re always interested in what they’re talking about.





“TNPD” doesn’t roll off the tongue as well as “TACO”, but I’ll take it.